Hierarchical geographical organization for efficient resource allocation
🗺️ Multi-Level Structure
Service areas support hierarchical organization (Region → District → Neighborhood). This enables flexible resource allocation, performance tracking at multiple levels, and efficient geographical optimization. Perfect for organizations of all sizes.
📍 Geographical Boundaries
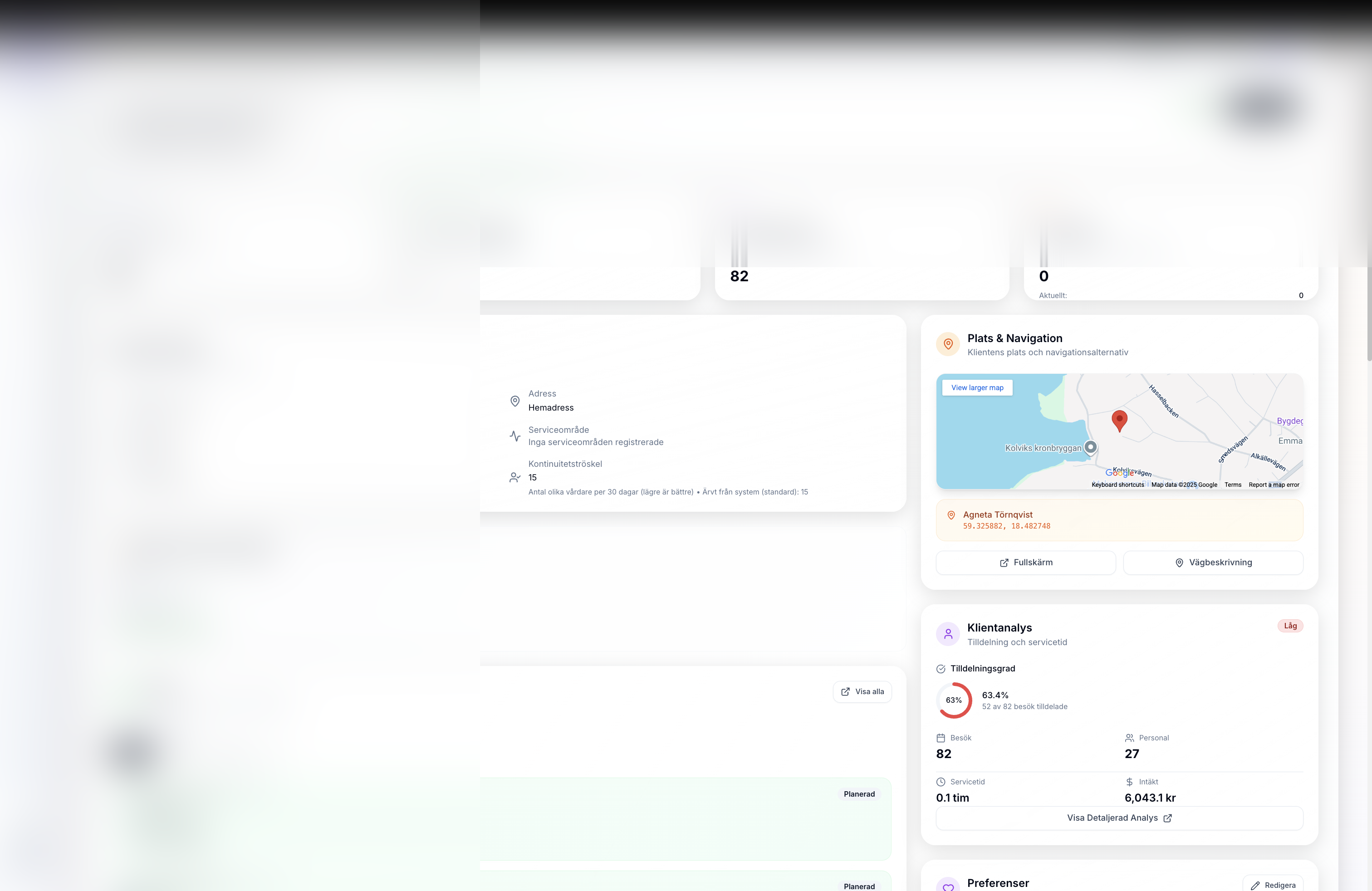
Define service area boundaries for accurate route optimization and resource allocation planning.
👥 Staff Assignment
Assign employees to specific service areas. Track staff count and utilization per area for balanced workload.
📊 Performance Tracking
Monitor visit metrics, assignment rates, time analytics, staff utilization, and financial performance for each service area.
🔗 Parent-Child Relationships
Maintain hierarchical service area structure. Aggregate metrics roll up from child to parent areas for comprehensive reporting.
💰 Financial Metrics
Track revenue, costs, and margins per service area. Identify profitable areas and improvement opportunities.
⚡ Optimization Integration
Service areas feed directly into AI optimization. Geographical constraints ensure realistic routing and travel time calculations.
🔄 Cross-Area Assignments
Configure whether employees can be assigned visits across service area boundaries. Enable for flexibility, disable for strict geographic separation.
🚫 Import Filtering
Disable specific service areas from import/optimization (e.g., administrative areas, analytics-only regions). Excluded areas maintain data but don't participate in scheduling.
Service Area Configuration Settings
Operational Settings per Service Area:
| Setting |
Description |
Default |
Impact |
| Cross-Service Area Assignments |
Allow employees to be assigned visits across different service areas |
Disabled |
When enabled: Staff can work in multiple areas (flexibility). When disabled: Staff only assigned to their home service area (geographic separation). |
| Include in Import |
Include this service area in automatic imports from external systems |
Enabled |
When disabled: Area excluded from nightly imports and optimization (useful for admin areas, testing areas, or analytics-only regions). |
| Include in Optimization |
Include this service area in AI optimization runs |
Enabled |
When disabled: Area maintains data but doesn't participate in scheduling (useful for inactive areas or regions under restructuring). |
| Default Hourly Rate |
Service area-level hourly rate override |
Organization default |
Override for high-cost areas (urban vs rural compensation differences). |
Cross-Area Assignment Example:
Scenario: North and South Service Areas
Cross-Area Disabled (Default):
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
North Area:
- Staff: 15 employees assigned to North
- Visits: 220 visits in North
- Assignment rule: North staff → North visits only
- Utilization: 80% (high)
South Area:
- Staff: 12 employees assigned to South
- Visits: 123 visits in South
- Assignment rule: South staff → South visits only
- Utilization: 40% (low)
Result: Geographic separation maintained, but imbalance exists
Cross-Area Enabled:
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Optimization runs across unified pool:
- All 27 staff can be assigned to any visit (North or South)
- System shifts 2 South staff to North high-demand area
- North: 17 staff, 220 visits = 94% utilization (better!)
- South: 10 staff, 123 visits = 70% utilization (better!)
Trade-off:
- Better utilization balance
- Slightly longer travel for shifted staff
- Less familiar with cross-area customers initially
Use when: Staff shortage in one area, geographic imbalance, flexibility needed
Import Filtering Example:
Organization: Regional Health Services
Service Areas:
1. North Operations (Include in Import: ✓, Include in Optimization: ✓)
2. South Operations (Include in Import: ✓, Include in Optimization: ✓)
3. Central Admin (Include in Import: ✗, Include in Optimization: ✗)
4. Analytics Test Area (Include in Import: ✗, Include in Optimization: ✗)
Nightly Import Results:
- North: 220 visits imported and optimized ✓
- South: 123 visits imported and optimized ✓
- Central Admin: Skipped (admin area only, no field operations)
- Analytics Test: Skipped (testing area, not production)
Benefits:
- Clean optimization (only operational areas)
- No need to manually exclude admin areas
- Analytics areas can exist for reporting without affecting schedules
- Faster optimization (fewer resources to process)